Short-term liabilities, also known as current liabilities, are obligations or debts that a company expects to settle within a year or its operating cycle, whichever is longer. Accounts payable are amounts owed to suppliers for goods or services received but not yet paid for. These can provide businesses with necessary working capital for day-to-day operations. Companies must carefully monitor their payment obligations and ensure they have sufficient liquidity to meet these obligations on time. Monitoring and managing these liabilities are essential for maintaining a healthy financial position and avoiding potential disruptions in cash flow.
What Are Liabilities? (Definition, Examples, and Types)
The borrowing of funds to expand the business may be viewed as a positive liability. A business’s liabilities can be examined in a variety of ways to determine its overall health and long-term viability. A summary of liability types can be found in the illustration below. For example, a manufacturing company with two owned warehouses may decide they need three owned warehouses to keep up with growing product demand. Therefore, the company issues bonds to help pay for the additional warehouse.
Example of Current Liabilities
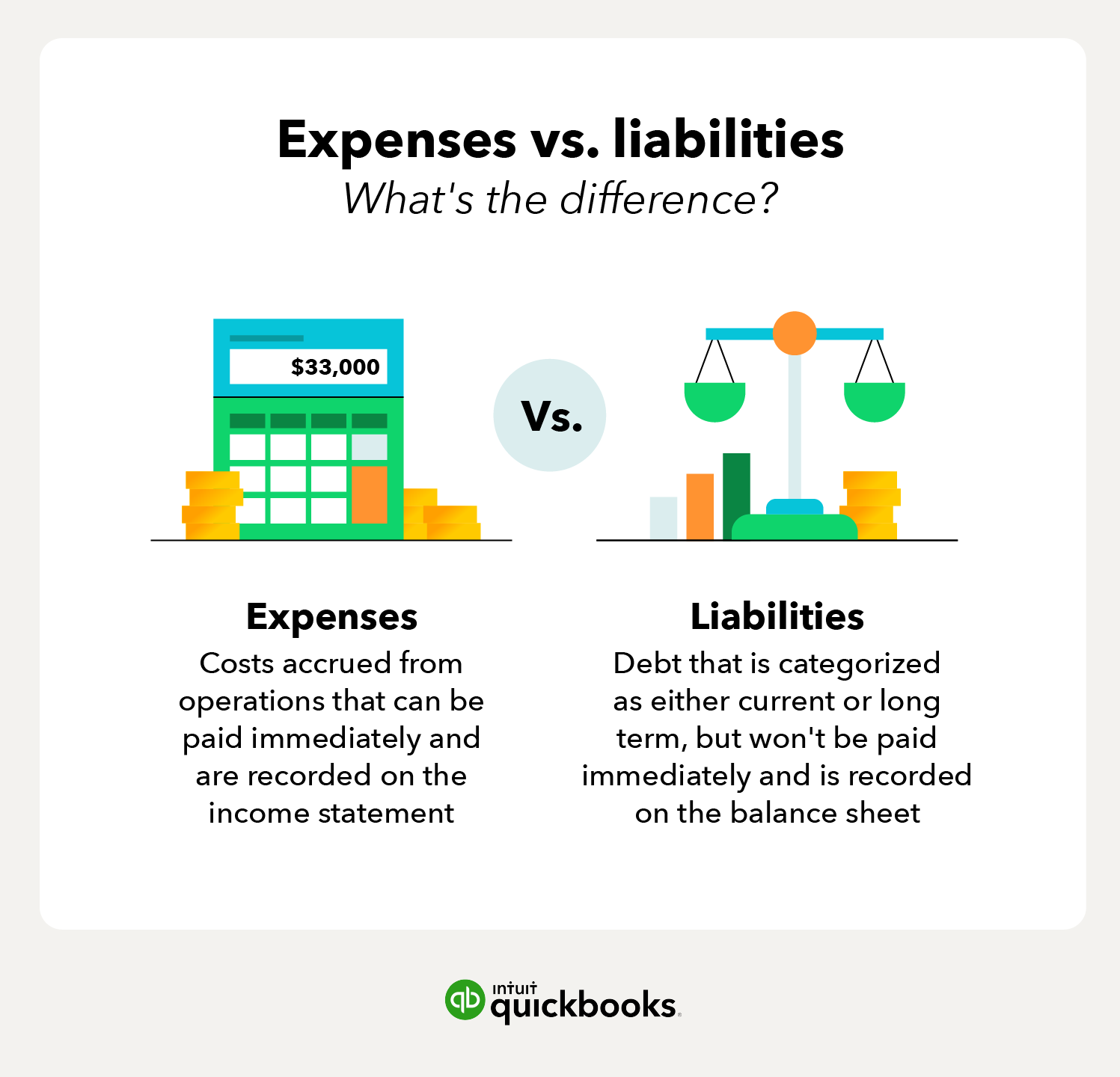
Long-term liabilities are debts that take longer than a year to repay, including deferred current liabilities. Contingent liabilities are potential liabilities that depend on the outcome of future events. For example contingent liabilities can become current or long-term if realized. By far the most important equation in credit accounting is the debt ratio. It compares your total liabilities to your total assets to tell you how leveraged—or, how burdened by debt—your business is. An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue.
Why Is Accounts Payable a Current Liability?
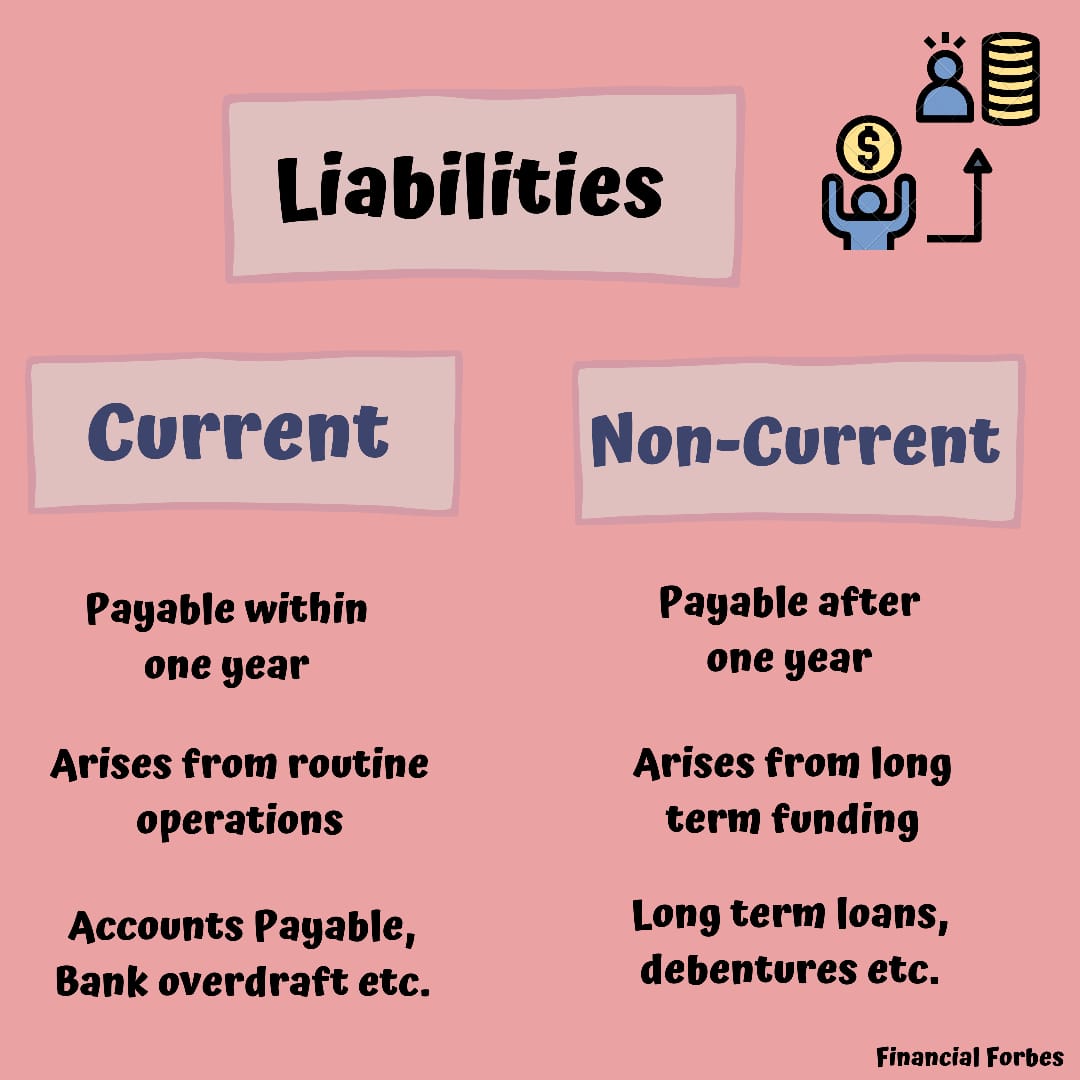
On the balance sheet, total assets minus total liabilities equals equity. Long-term liabilities are financial obligations of a company that extends more than a year. These liabilities affect a company’s financial structure because they indicate the amount of debts you have acquired to finance your assets and business operations. Accrued expenses are listed in the current liabilities section of the balance sheet because they represent short-term financial obligations. Companies typically will use their short-term assets or current assets such as cash to pay them. Current liabilities of a company consist of short-term financial obligations that are typically due within one year.
What Are the Different Types of Liabilities in Accounting?
If you want to check the financial performance of a company in relation to assets and liabilities, check the balance sheet. When you borrow funds, you’ll have to pay interest to the creditor. However, other liabilities such as accounts payable often don’t have interest charges since these are due in less than six months. In liabilities examples very specific contract liabilities, failure to pay on the installment date will produce penalties, and such penalties can also be considered a cost of having liabilities. It can appear like spending and liabilities are the same thing, but they’re not. Expenses are what your organization regularly pays to fund operations.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
These are long-term liabilities that arise from differences between accounting income and taxable income, leading to taxes owed in the future. For instance, when a company uses different methods for reporting income for tax purposes and financial reporting, it can create a deferred tax liability. This topic involves understanding how timing differences affect tax obligations and the importance of recognizing these liabilities in financial statements.
This is often used as operating capital for day-to-day operations by a company of this size rather than funding larger items which would be better suited using long-term debt. Liability generally refers to the state of being responsible for something. Tax liability can refer to the property taxes that a homeowner owes to the municipal government or the income tax they owe to the federal government.
Unearned revenue is money received or paid to a company for a product or service that has yet to be delivered or provided. Unearned revenue is listed as a current liability because it’s a type of debt owed to the customer. Once the service or product has been provided, the unearned revenue gets recorded as revenue on the income statement. Current liabilities are expected to be paid back within one year, and long-term liabilities are expected to be paid back in over one year.
- This topic involves understanding how timing differences affect tax obligations and the importance of recognizing these liabilities in financial statements.
- The working capital of a company is obtained by subtracting the current liabilities from the current assets.
- These obligations may arise due to specific situations and conditions.
- Liabilities are carried at cost, not market value, like most assets.
In addition, liabilities facilitate and more efficiently allow transactions between businesses. Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
In the case of liabilities, the “other” tag can refer to things like intercompany borrowings and sales taxes. Because payment is due within a year, investors and analysts are keen to ascertain that a company has enough cash on its books to cover its short-term liabilities. However, if one company’s debt is mostly short-term debt, it might run into cash flow issues if not enough revenue is generated to meet its obligations. Many first-time entrepreneurs are wary of debt, but for a business, having manageable debt has benefits as long as you don’t exceed your limits.